環境設置
在開始寫 C++ 程式之前,我們需要設置好開發環境, 原因是我們的電腦其實讀不懂 C++ 程式碼, 我們需要一個工具——編譯器, 它可以將我們寫的 C++ 程式碼轉換成電腦可以理解的機器碼, 然後電腦才能執行這些程式。
筆者假設大部分的讀者皆是剛入門程式設計的同學, 這裡介紹的第一種方法 CP Editor 比較簡單,不用過多的設定, 但只適用於程式競賽課程,如果你之後也有打算寫其他程式語言, 建議你使用 Visual Studio Code 這個編輯器, 它是目前最流行的程式編輯器之一,支援多種程式語言, 並且有許多擴充功能可以使用。
CP Editor
CP Editor 是一個專門用於程式競賽的輕量化編輯器,專門為程式競賽設計,因為下載的時候還可以一起把編譯器環境打包好,不用自己設定,所以在這裡介紹給初學者使用,這個軟體同時也是南臺灣學生資訊社群 (SCIST) 的指定編輯器。
安裝 CP Editor
- 前往 CP Editor 官方網站。
- 點擊「下載軟體」按鈕,選擇適合你作業系的版本(Windows、macOS 或 Linux)。
- 選擇帶有
with-gcc字樣的安裝檔進行下載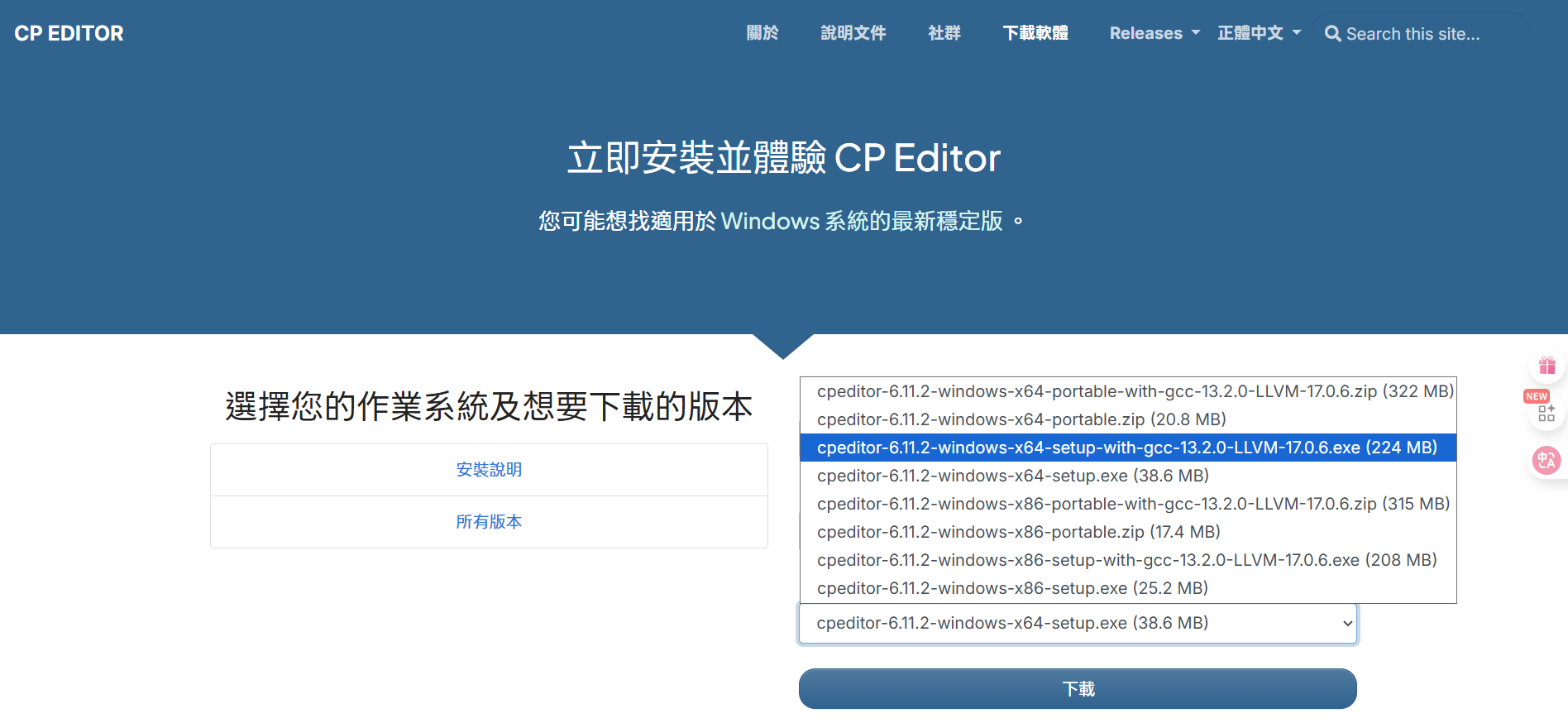
- 下載完成後,去到下載的資料夾雙擊安裝檔,按照指示完成安裝。
安裝完畢之後就可以開始使用 CP Editor 了。
設定 CP Editor
- 打開 CP Editor,點擊左上角的 "Options" > "Preferences"。
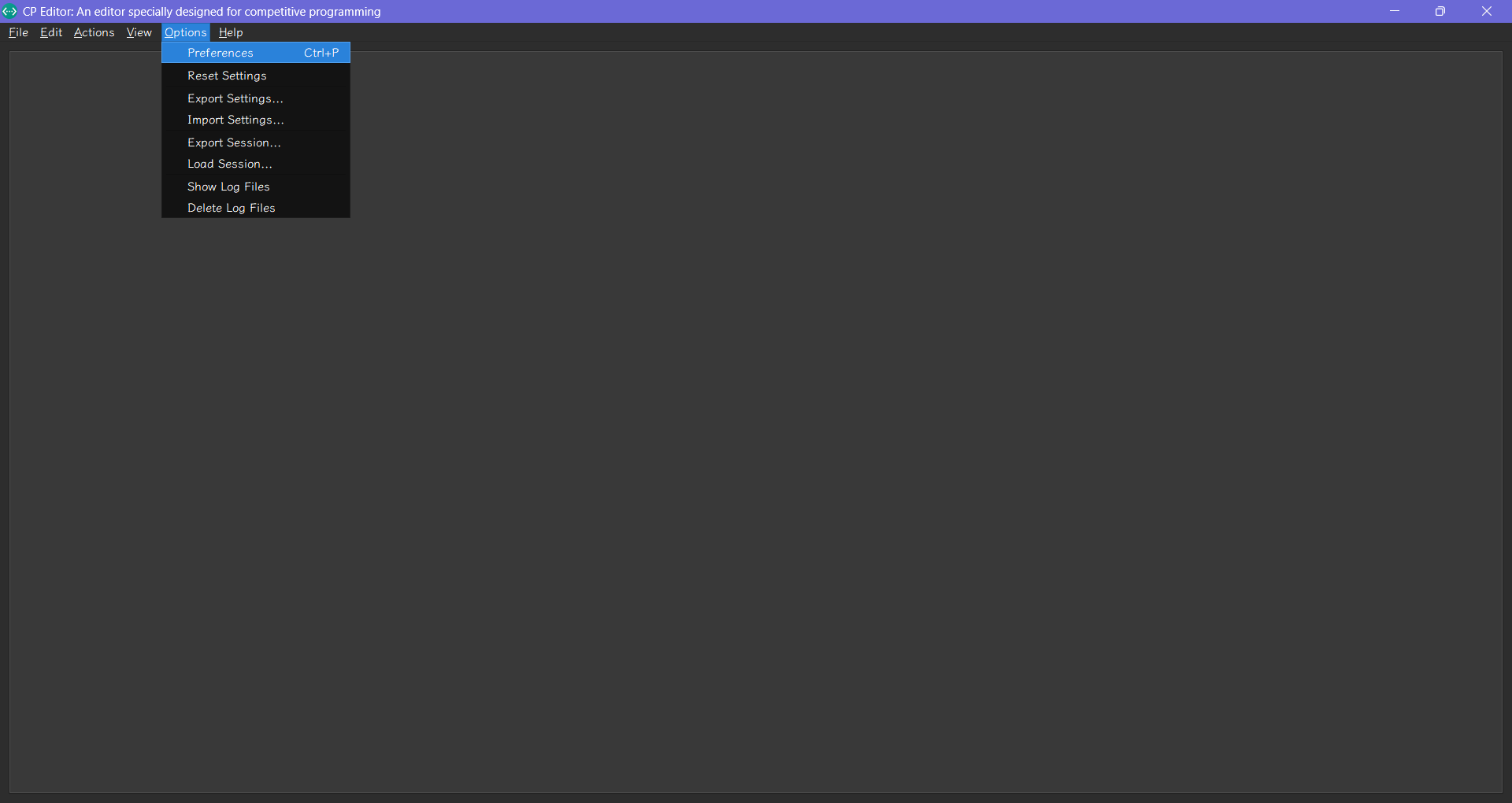
- 選擇 "Appearance" > "General",選擇 "正體中文" 作為語言。
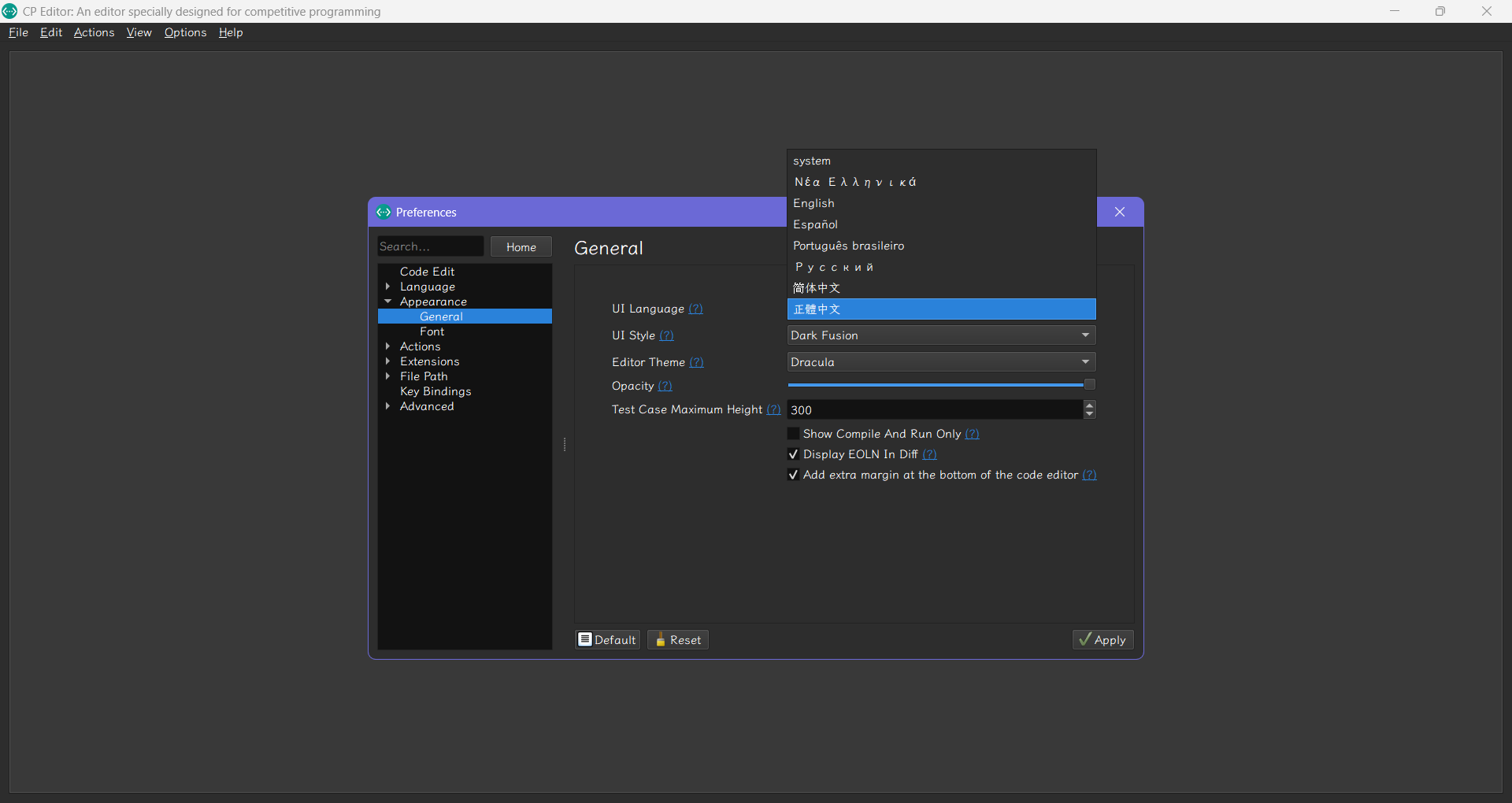
- 重開 CP Editor,你會看到介面已經變成中文了。接著我們回到 "選項" > "偏好設定",在 "動作" > "測資" 中,勾選測資輸入為空時仍然執行。
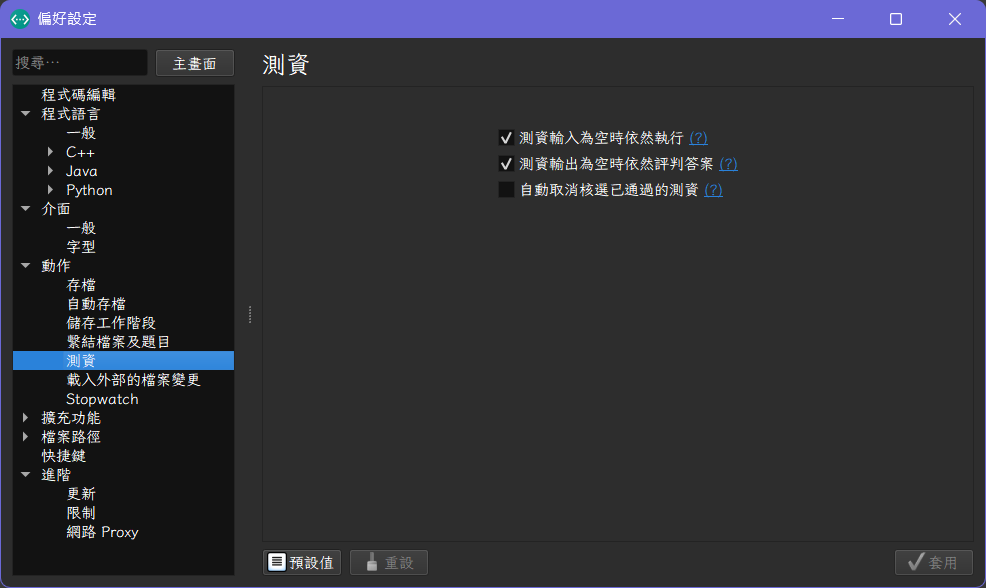
- 套用後回到主畫面,點擊左上角的 "檔案" > "新檔案",按下
Ctrl + S儲存檔案,將檔案命名為main.cpp,這是 C++ 的標準檔案名稱,放在一個你想要的資料夾中。 - 將範例程式碼複製到
main.cpp中:
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::cout << "Hello world!\n";
return 0;
}
- 點擊編譯並執行按鈕,CP Editor 會自動編譯並執行你的程式,並在右方的輸出視窗中顯示結果。
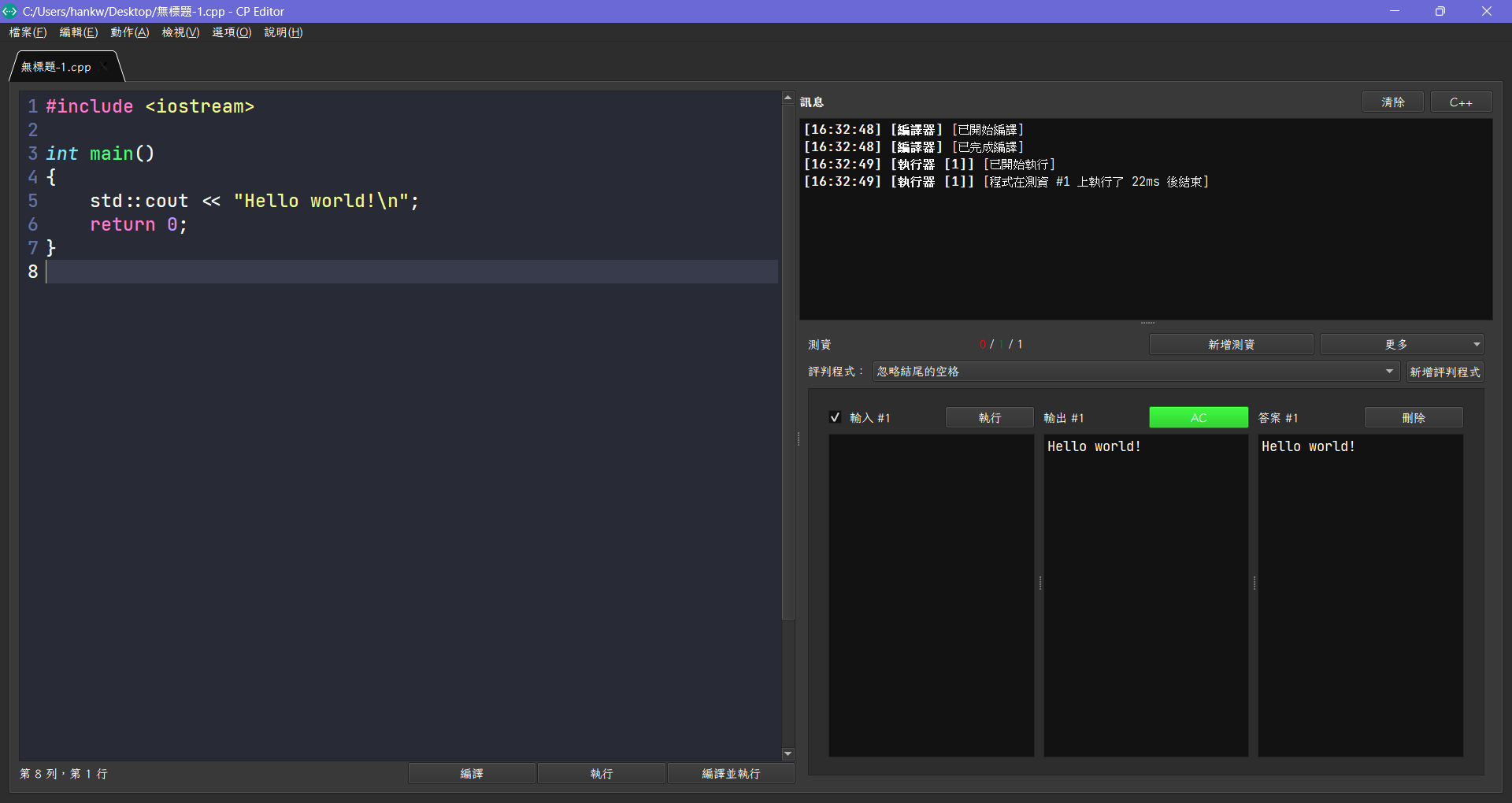
- 如果一切順利,你應該會看到輸出結果為
Hello world!。
至此,你已經成功設置了 CP Editor 開發環境, 並且可以開始寫 C++ 程式了。
如果你使用 Windows 系統,有時候防毒軟體會誤判 C++ 編譯產生的執行檔為
病毒,這是因為 C++ 編譯器會生成一個可執行檔,這個檔案有時候會被防毒軟體誤判為病毒,我建議大家選擇一個資料夾 (假設是桌面上某個 cpp_learning 資料夾),然後點開 Windows 安全性 的防毒軟體設定,將這個資料夾加入白名單,這樣就不會被誤判了。
- 點擊
病毒與威脅防護>病毒與威脅防護設定>管理設定。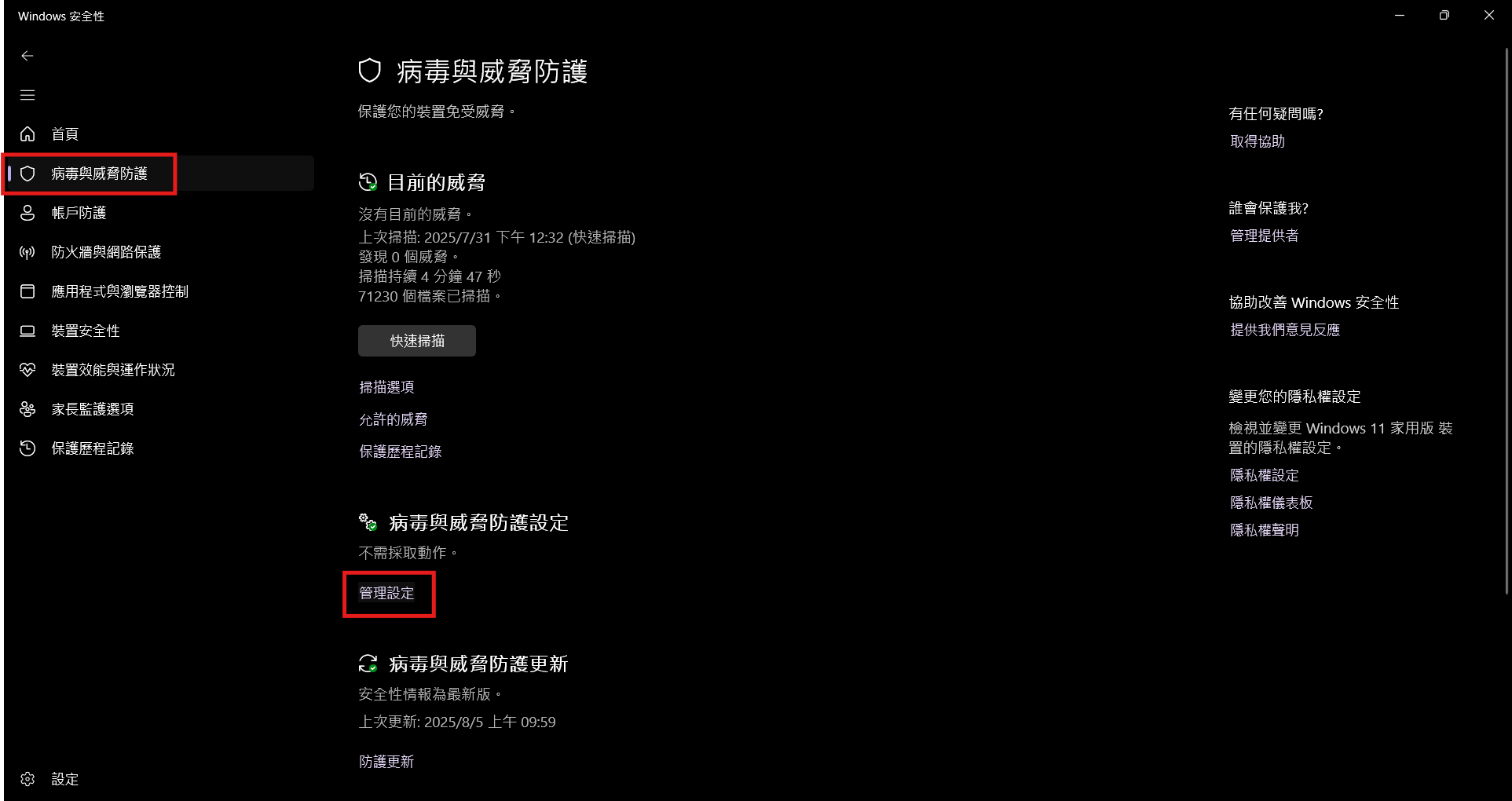
- 在
排除項目中點擊新增或移除排除項目。 - 將剛剛建立的
cpp_learning資料夾加入排除項目。
這樣就可以避免防毒軟體誤判 C++ 編譯器生成的執行檔為病毒了。
Visual Studio Code
Visual Studio Code (下稱 VS Code) 是一個由微軟開發的免費開源程式碼編輯器,支援多種程式語言,包括 C++。它有許多強大的功能,如語法高亮、程式碼補全、除錯等。但因為 VS Code 本身並不包含 C++ 編譯器,所以我們需要額外安裝一些東西來讓它能夠編譯和執行 C++ 程式。
安裝 LLVM MinGW
LLVM MinGW 是一個 C++ 編譯器,是一個支援跨平台的編譯器,剛才的 CP Editor 就是使用這個編譯器來編譯 C++ 程式的, 但是因為 VS Code 本身並不包含 C++ 編譯器,所以我們需要額外安裝 LLVM MinGW。
- 前往 LLVM MinGW GitHub 頁面 下載最新版本的 Prebuilt LLVM MinGW。
- 找到 "Latest" 字樣的版本,點擊進入,尋找對應你作業系統的壓縮檔案,這裡以 Windows 為例,下載
llvm-mingw-<version>-x86_64.zip。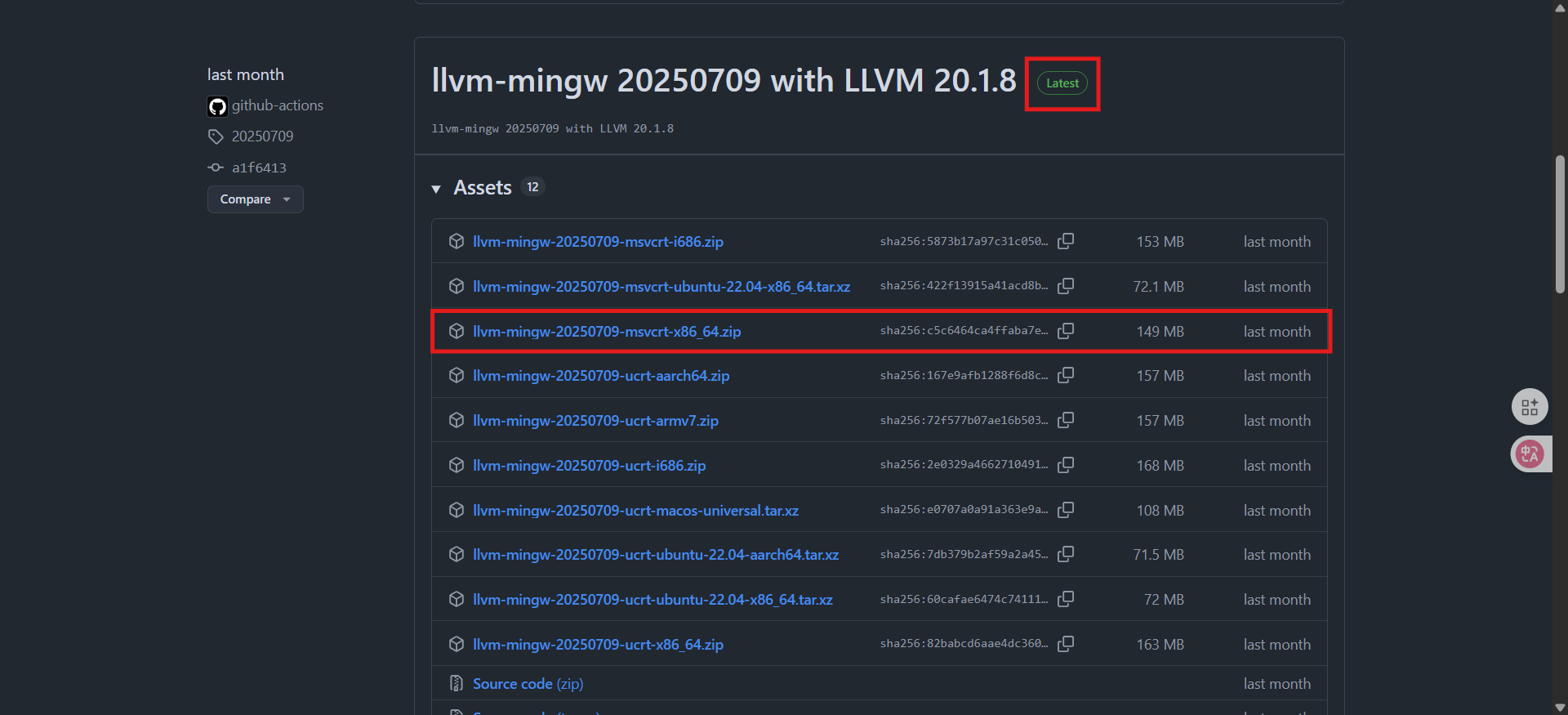
- 直接解壓縮後放到你想要的資料夾中,例如
C:\llvm-mingw。 - 接著需要將 LLVM MinGW 的
bin資料夾加入系統的環境變數中,這樣 VS Code 才能找到編譯器。- 在 Windows 中,進入設定面板,搜尋 「環境變數」。
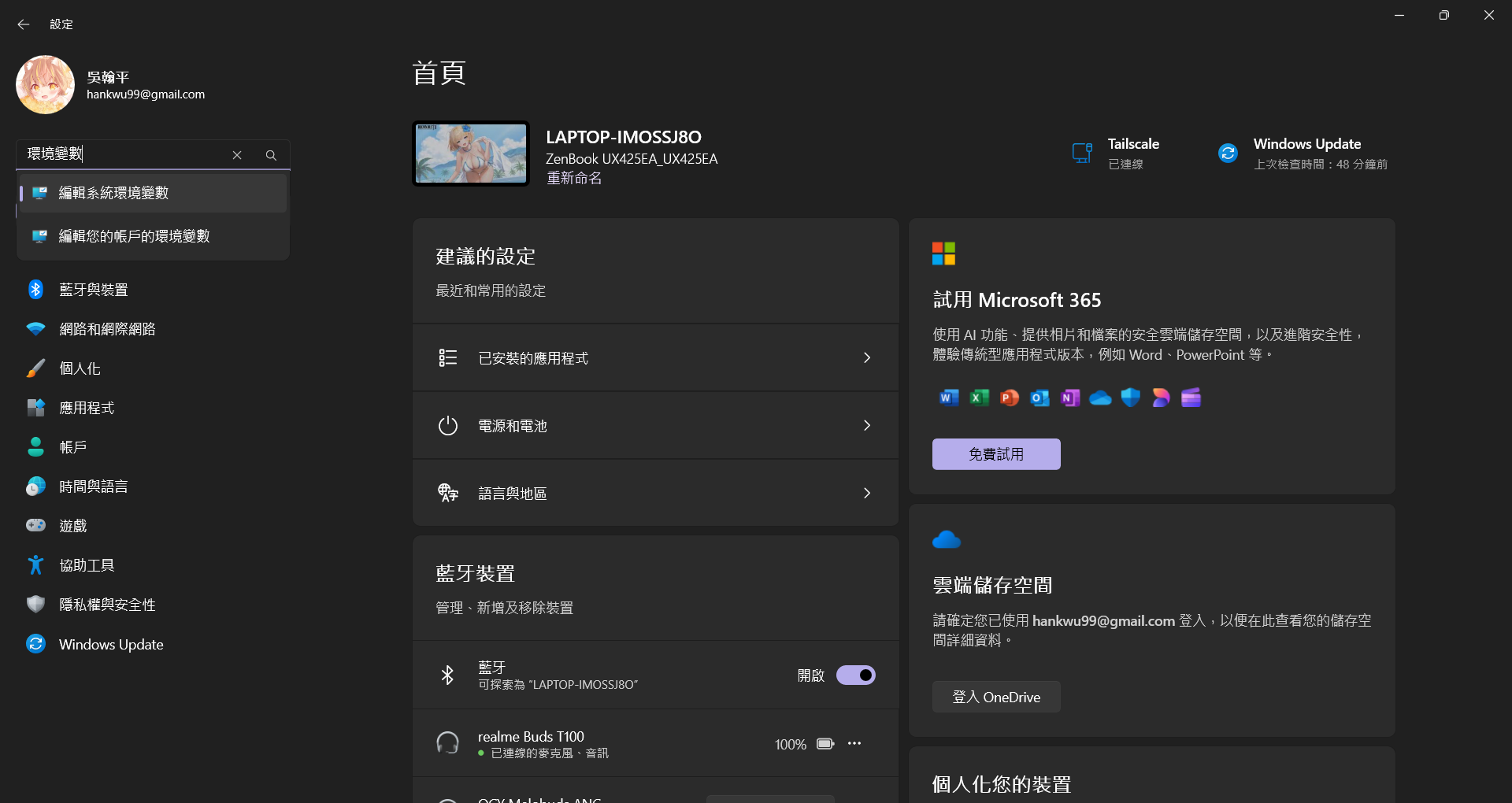
- 在對話框中,點擊「環境變數」。
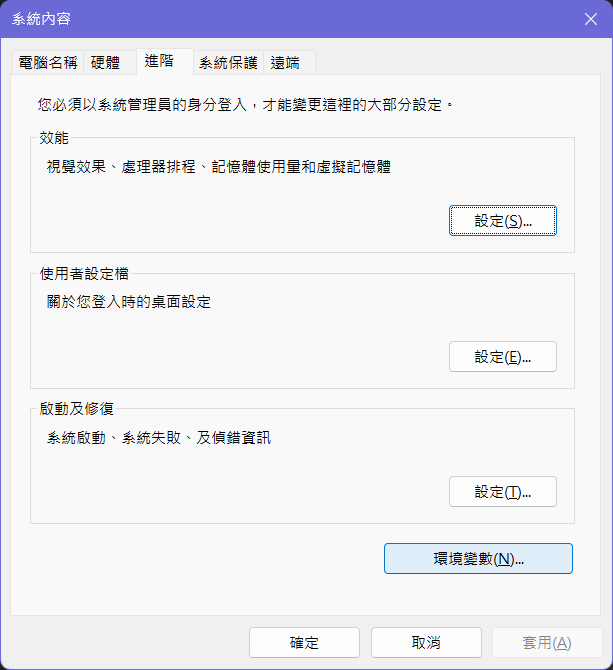
- 在「系統變數」區域,找到名為
Path的變數,選擇它並點擊「編輯」。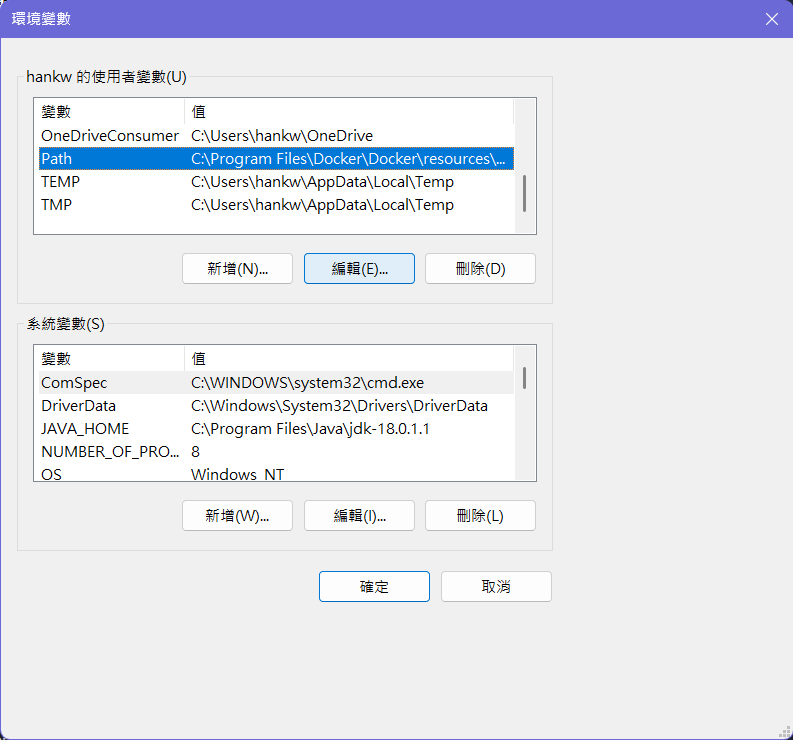
- 點擊「新增」,然後輸入 LLVM MinGW 的
bin資料夾的路徑,例如C:\llvm-mingw\bin。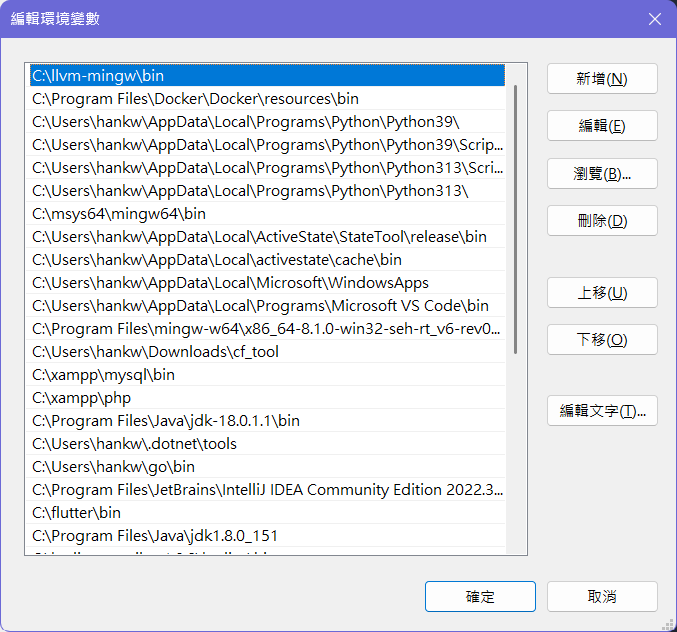
- 點擊「確定」保存更改。
- 在 Windows 中,進入設定面板,搜尋 「環境變數」。
- 為了確保環境變數生效,建議重新啟動電腦,接著打開命令提示字元 (CMD),輸入
g++ --version,如果顯示出版本資訊,表示 LLVM MinGW 安裝成功。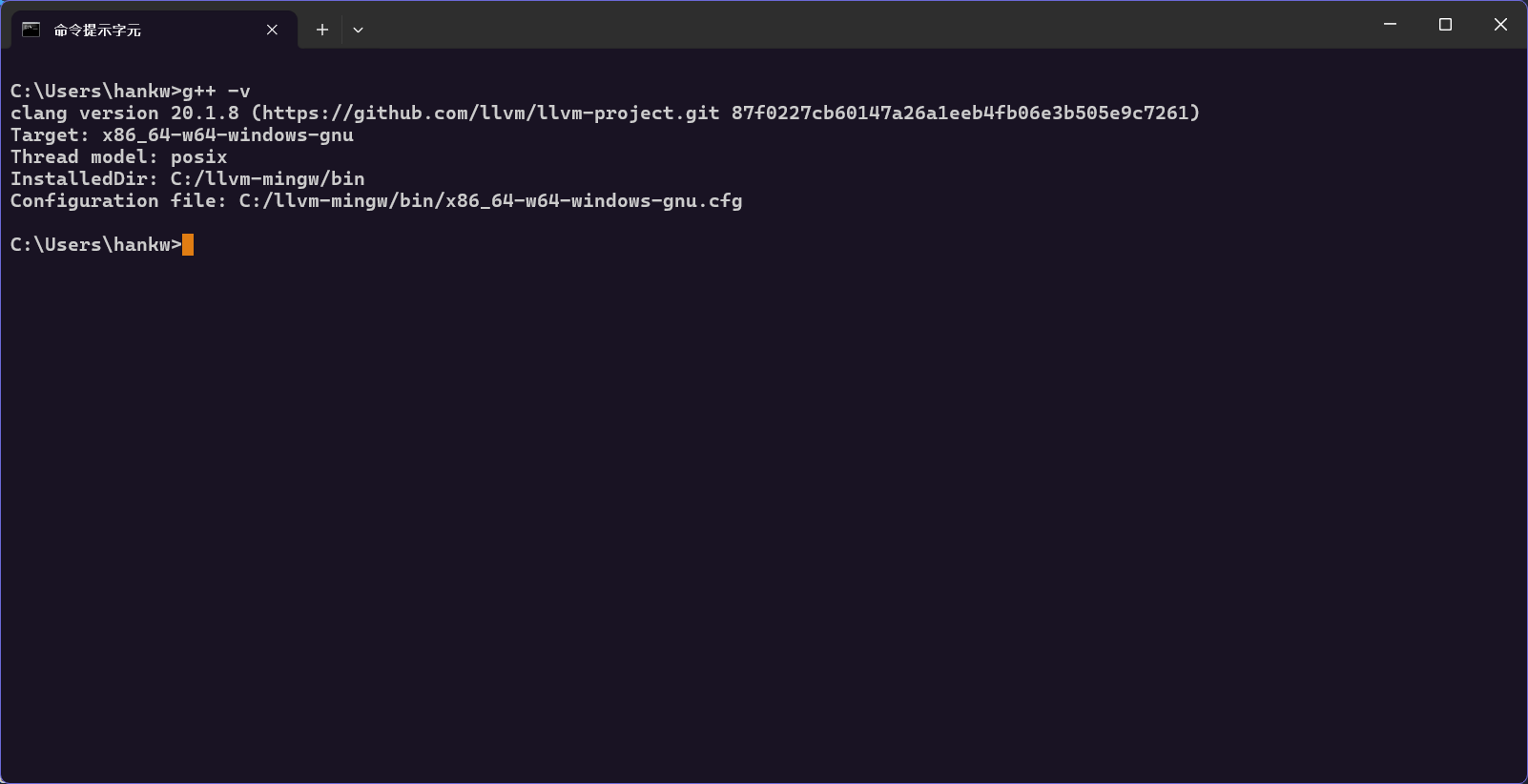
安裝 Visual Studio Code
- 前往 Visual Studio Code 官方網站 進行下載
- 點擊「Download for Windows」按鈕,下載適合你作業系統的安裝檔。
- 下載完成後,雙擊安裝檔,按照指示完成安裝。
- 因為 VS Code 也會新增一些環境變數,所以建議重新啟動電腦。
- 打開 VS Code,點擊左側的擴充功能圖示 (Extensions),搜尋
C/C++,安裝由 Microsoft 提供的 C/C++ 擴充套件。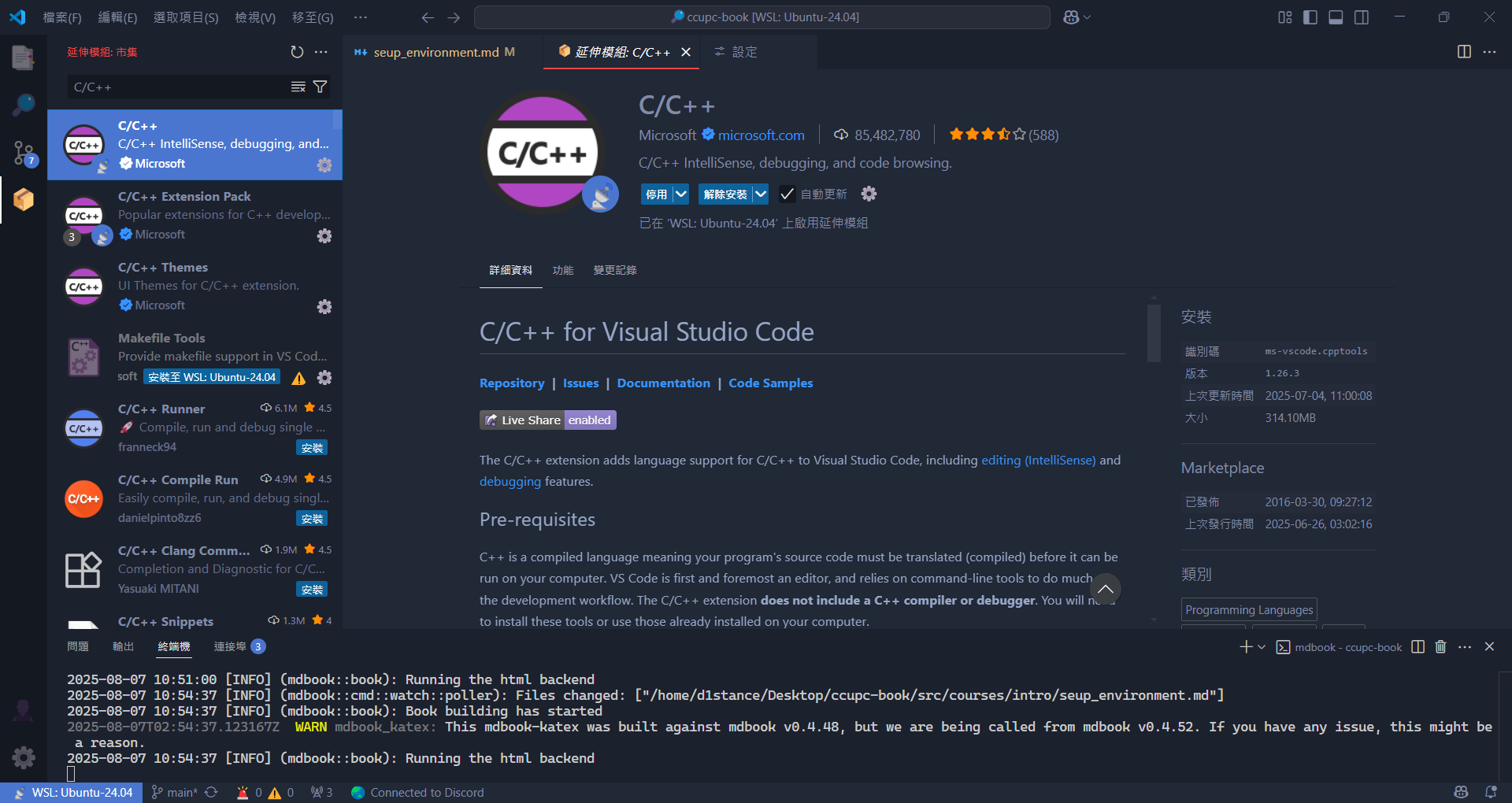
- 安裝好後點擊齒輪 > 設定 (Settings) > 在上方搜尋框輸入 "Compiler Path"
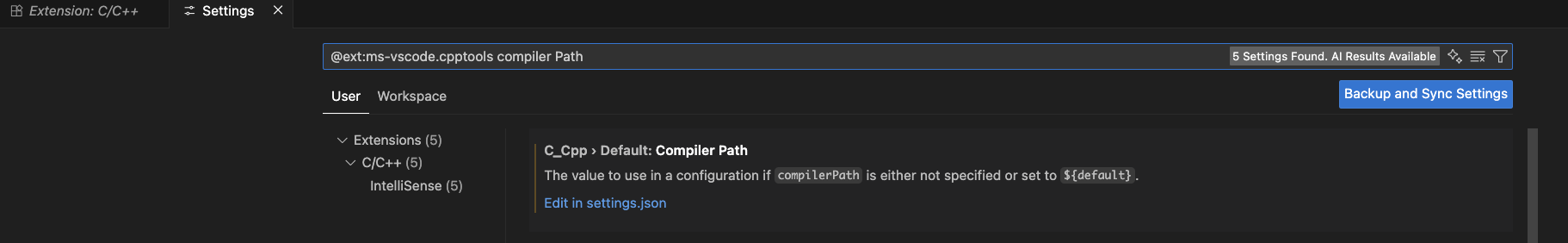
- 將 "C_Cpp.default.compilerPath" 冒號後的路徑填入你剛才在環境變數設置的路徑,結尾加上 g++.exe,像是
C:\llvm-mingw\bin\g++.exe - 存檔後關閉設定,這樣以後寫 C++ 就會有語法提示了。
- 接著新增一個 C++ 檔案,點擊左上角的「檔案」>「新檔案」,將檔案儲存為
main.cpp。 - 將範例程式碼複製到
main.cpp中:
#include <iostream>
int main()
{
std::cout << "Hello world!\n";
return 0;
}
並且記得存檔
- 接著按下
Ctrl + ‵,開啟終端機,然後輸入以下指令來編譯程式:
g++ main.cpp -o main
這個指令會將 main.cpp 編譯成一個可執行檔 main.exe。
9. 編譯完成後,輸入以下指令來執行程式:
main.exe
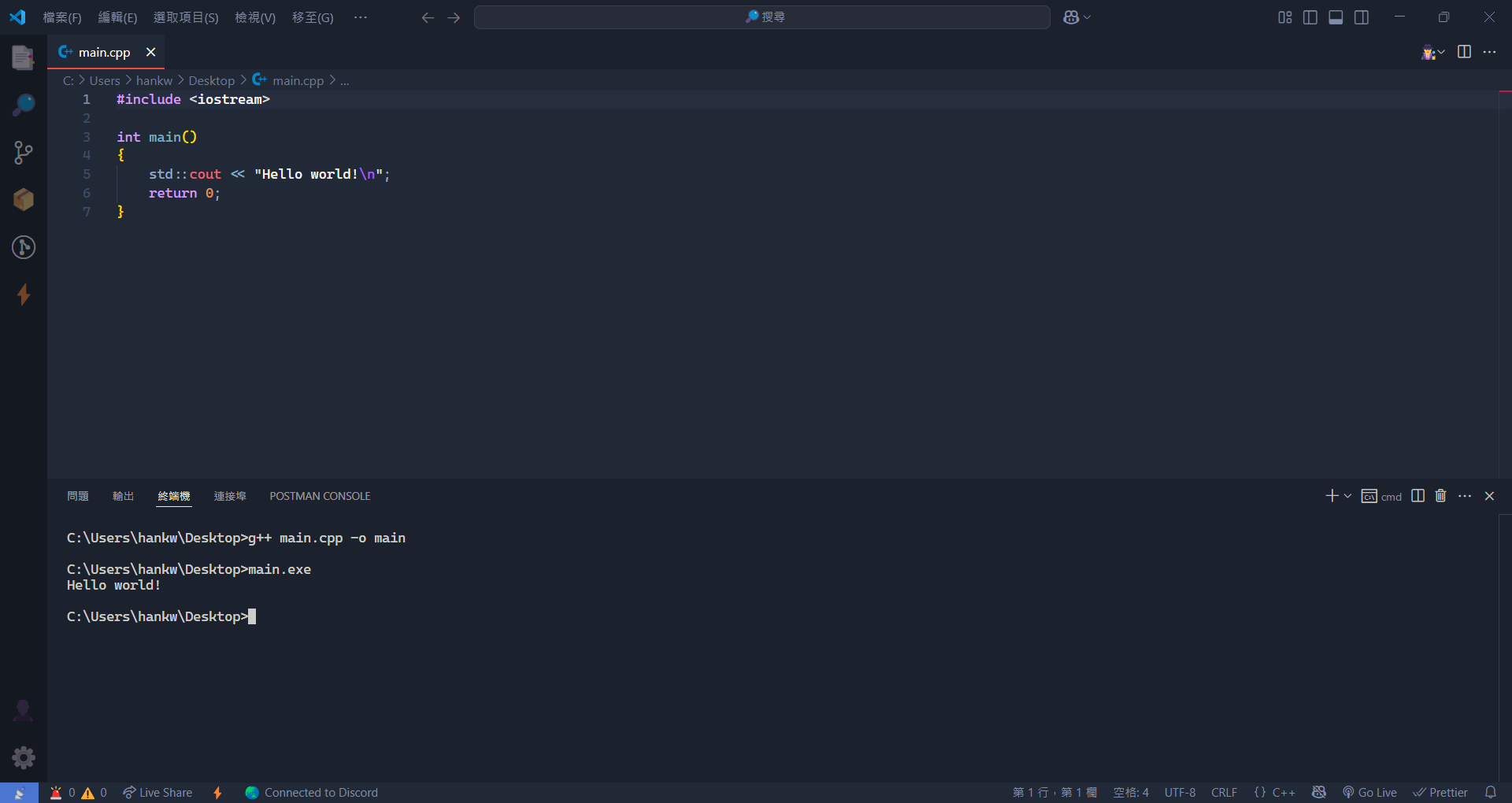 如果一切順利,你應該會看到輸出結果為
如果一切順利,你應該會看到輸出結果為 Hello world!。
到此,你已經成功設置了 Visual Studio Code 開發環境, 並且可以開始寫 C++ 程式了。
如何啟用 #include <bits/stdc++.h>
因為 CP Editor 和 Visual Studio Code 都是使用 LLVM MinGW 作為編譯器,
這個編譯器是基於 Clang 的,而 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 是 GCC 編譯器的專有標頭檔,
所以在 LLVM MinGW 中並沒有這個標頭檔。
如果要使用這個競程萬用標頭檔,可以在 llvm-mingw/include 下手動建立一個 bits 資料夾,
然後在這個資料夾中建立一個 stdc++.h 檔案,並將以下內容複製到這個檔案中:
// C++ includes used for precompiling -*- C++ -*-
// Copyright (C) 2003-2025 Free Software Foundation, Inc.
//
// This file is part of the GNU ISO C++ Library. This library is free
// software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the
// terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the
// Free Software Foundation; either version 3, or (at your option)
// any later version.
// This library is distributed in the hope that it will be useful,
// but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of
// MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the
// GNU General Public License for more details.
// Under Section 7 of GPL version 3, you are granted additional
// permissions described in the GCC Runtime Library Exception, version
// 3.1, as published by the Free Software Foundation.
// You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License and
// a copy of the GCC Runtime Library Exception along with this program;
// see the files COPYING3 and COPYING.RUNTIME respectively. If not, see
// <http://www.gnu.org/licenses/>.
/** @file stdc++.h
* This is an implementation file for a precompiled header.
*/
// 17.4.1.2 Headers
// C
#ifndef _GLIBCXX_NO_ASSERT
#include <cassert>
#endif
#include <cctype>
#include <cfloat>
#include <climits>
#include <csetjmp>
#include <cstdarg>
#include <cstddef>
#include <cstdlib>
#if __cplusplus >= 201103L
#include <cstdint>
#if __cplusplus < 201703L
#include <ciso646>
#endif
#endif
// C++
// #include <bitset>
// #include <complex>
#include <algorithm>
#include <bitset>
#include <functional>
#include <iterator>
#include <limits>
#include <memory>
#include <new>
#include <numeric>
#include <typeinfo>
#include <utility>
#if __cplusplus >= 201103L
#include <array>
#include <atomic>
#include <initializer_list>
#include <ratio>
#include <scoped_allocator>
#include <tuple>
#include <typeindex>
#include <type_traits>
#endif
#if __cplusplus >= 201402L
#endif
#if __cplusplus >= 201703L
#include <any>
// #include <execution>
#include <optional>
#include <variant>
#include <string_view>
#endif
#if __cplusplus >= 202002L
#include <bit>
#include <compare>
#include <concepts>
#include <numbers>
#include <ranges>
#include <span>
#include <source_location>
#include <version>
#if __cpp_impl_coroutine
# include <coroutine>
#endif
#endif
#if __cplusplus > 202002L
#include <expected>
#include <stdatomic.h>
#endif
// C
#ifndef _GLIBCXX_NO_ASSERT
#include <cassert>
#endif
#include <cctype>
#include <cerrno>
#include <cfloat>
#include <climits>
#include <clocale>
#include <cmath>
#include <csetjmp>
#include <csignal>
#include <cstdarg>
#include <cstddef>
#include <cstdio>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <cstring>
#include <ctime>
#include <cwchar>
#include <cwctype>
#if __cplusplus >= 201103L
#include <cfenv>
#include <cinttypes>
#include <cstdint>
#include <cuchar>
#if __cplusplus < 201703L
#include <ccomplex>
#include <cstdalign>
#include <cstdbool>
#include <ctgmath>
#endif
// C++
#include <complex>
#include <deque>
#include <exception>
#include <fstream>
#include <functional>
#include <iomanip>
#include <ios>
#include <iosfwd>
#include <iostream>
#include <istream>
#include <iterator>
#include <limits>
#include <list>
#include <locale>
#include <map>
#include <memory>
#include <new>
#include <numeric>
#include <ostream>
#include <queue>
#include <set>
#include <sstream>
#include <stack>
#include <stdexcept>
#include <streambuf>
#include <string>
#include <typeinfo>
#include <utility>
#include <valarray>
#include <vector>
#if __cplusplus >= 201103L
#include <array>
#include <atomic>
#include <chrono>
#include <codecvt>
#include <condition_variable>
#include <forward_list>
#include <future>
#include <initializer_list>
#include <mutex>
#include <random>
#include <ratio>
#include <regex>
#include <scoped_allocator>
#include <system_error>
#include <thread>
#include <tuple>
#include <typeindex>
#include <type_traits>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <unordered_set>
#endif
#if __cplusplus >= 201402L
#include <shared_mutex>
#endif
#if __cplusplus >= 201703L
#include <any>
#include <charconv>
// #include <execution>
#include <filesystem>
#include <optional>
#include <memory_resource>
#include <variant>
#endif
#if __cplusplus >= 202002L
#include <barrier>
#include <bit>
#include <compare>
#include <concepts>
#include <format>
#include <latch>
#include <numbers>
#include <ranges>
#include <span>
#include <stop_token>
#include <semaphore>
#include <source_location>
#include <syncstream>
#include <version>
#endif
#if __cplusplus > 202002L
#include <expected>
#include <flat_map>
#include <flat_set>
#include <generator>
#include <mdspan>
#include <print>
#include <spanstream>
#include <stacktrace>
#include <stdatomic.h>
#include <stdfloat>
#endif
#if __cplusplus > 202302L
#include <inplace_vector>
#include <text_encoding>
#include <stdbit.h>
#include <stdckdint.h>
#endif
#endif // HOSTED